General characteristics
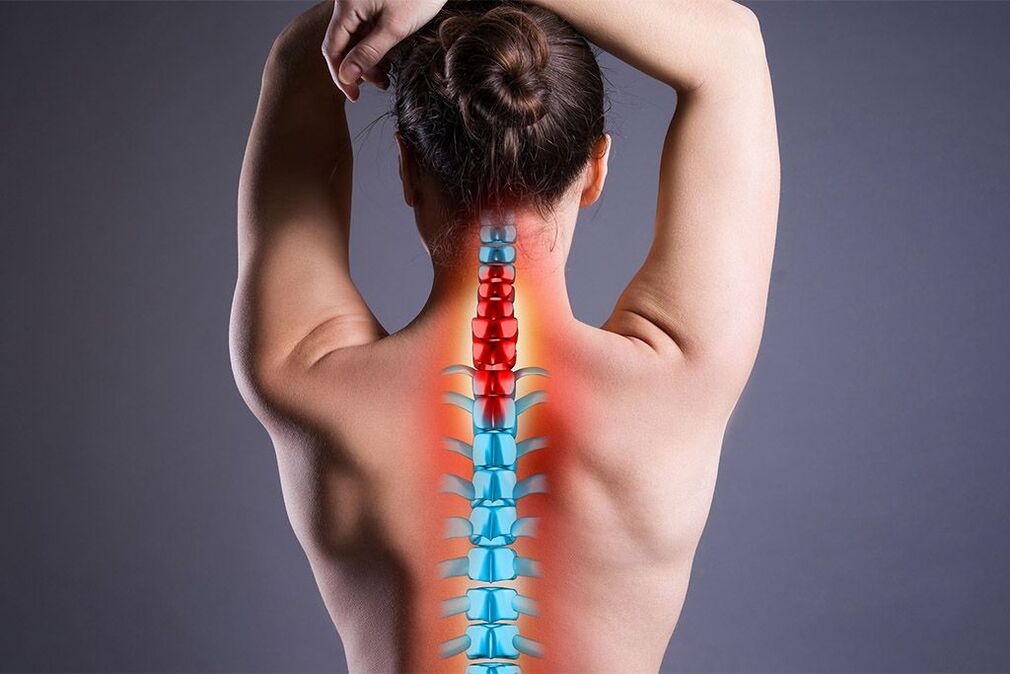
important! The pathology requires multidisciplinary control because it affects not only the musculoskeletal system but also the nervous system as well as the internal organs. In addition to the spine itself, pathological processes can affect other parts of the skeleton.
Etiology and pathogenesis
- Injuried;
- flatfoot;
- Clubfoot - a deformation of the foot (varus, varus, or valgus, depending on the position of the heel);
- Work related to weightlifting;
- Performing exercise without warming up or warming up muscles;
- Work at low temperatures.
symptom
- Unstable blood pressure;
- Headache;
- lack of coordination;
- hand pain;
- Numbness in upper body and arms.
- intercostal neuralgia;
- Stiffness in arms and neck;
- Internal organ dysfunction.
- combustion;
- urinary tract disorders;
- spasms; spasms;
- Pain when walking.
complication
- Spondyloarthropathy.
- Intervertebral disc degeneration.
- Spinal stenosis.
important! Intervertebral discs act as shock absorbers, reducing friction between vertebrae. Degenerative processes in these structures can lead to disc herniation and disc herniation. The protrusion can cause root pressure and pain.
- chronic pain in the spine;
- Friction of bone surfaces;
- rigidity;
- sudden muscle weakness;
- Reduced response;
- Tingling in the extremities;
- radiating pain;
- Sciatica symptoms.
Classification
- Class I - Pain easily relieved by medication.
- Degree II - Characterized by long-term pain and deformity of the spine with moderate neurological symptoms.
- Grade III - generalized pain with significant neurological symptoms.
- Degree IV - persistent pain, multiple neurologic deficits. Disorders of nerve impulse conduction. Paralysis and paresis.
| group | describe |
|---|---|
| First group | Loss of function of the spine. Patients are unable to move independently and care for themselves. |
| Second Group | The patient is able to move around and perform small tasks, but the condition often worsens. The surgery is contraindicated or useless for some reason. Or surgery has been performed, but the results were ineffective. |
| The third group | The patient has the ability to take care of himself. Pain and vestibular symptoms were present, but exacerbations were moderate and cyclical. |
Disability groups are assigned by doctors based on a number of studies assessing work ability.
diagnosis
- X-ray of the entire spine, divided into two projections.
- MRI is used to evaluate ligaments and nerve tissue.
- Electrophysiological studies that test nerve impulse conduction.
- Bone scan.
- Discography.
- Myelography.
treat
- Slows down the degenerative process by improving the supply of nutrients to the structures of the musculoskeletal system.
- The spine is stable.
- Eliminate compressed nerve fibers.
- Relieve symptoms.
- NSAIDs to relieve inflammation and pain;
- Anilides relieve pain in the initial stages;
- Topical analgesics in ointment form;
- Muscle relaxants reduce muscle spasms and increase range of motion;
- B vitamins improve nerve tissue conductivity;
- Chondroprotectant, reduces the rate of progression of degenerative processes by integrating active substances (chondroitin sulfate and glucosamine) into chondrocytes. As a result, metabolism normalizes and clinical manifestations decrease. This medicine has been used for a long time. People who are pregnant, breastfeeding, or have gastrointestinal diseases need special consultation. An absolute contraindication is phenylketonuria;
- Antispasmodics relieve smooth muscle spasms and thereby reduce the manifestations of osteochondrosis in internal organs;
- Antioxidants;
- Antidepressants can eliminate the psychosomatic components of the disease. They interfere with the transmission of nerve impulses from the central nervous system to the brain. Promotes the production of endorphins, which can help resolve chronic insomnia caused by persistent pain.
- Neuropathy drugs eliminate damage to nerve endings.
- Opioids are used to treat unbearable pain and conditions where other painkillers are ineffective.
- Steroids are injected into the epidural space. Steroids are powerful anti-inflammatory drugs. They can relieve inflammation in the nerve roots and help relieve pain caused by radiculopathy. The procedure is complex. Qualified experts are needed;
- Inject into facet joints. The injectable medication causes local numbness and pain relief.
It's important to understand this! Taking medications is not intended to eliminate the disease—no medications can completely eliminate osteochondrosis, which is a chronic condition. Medications are prescribed simply to relieve symptoms.
physiotherapy
- Electrophoresis (based on the movement of colloidal particles under the influence of an external electric field).
- Phonophoresis (a combination of ultrasound and medication).
- Magnetic therapy (using static magnetic fields).
- UHF therapy (Ultra High Frequency Therapy).
- Electrical muscle stimulation (stimulation of nerves and muscles).
- Acupuncture (acupuncture).
- Laser exposure.
Surgery
- Facetectomy – Removal of facet joints to relieve pressure.
- Foraminotomy increases the lumen of the spinal canal that is narrowed by osteophytes.
- A laminectomy is the removal of the back part of the vertebrae, which may be deformed by osteochondrosis.
- Laminotomy - Removal of fragments from the back of the vertebral body to enlarge the spinal canal.
- Discectomy – Removal of an intervertebral disc.
- Corpectomy – removal of the entire vertebral body and adjacent discs.
- Spinal fusion is a method of fusing the vertebrae.
- Artificial disc.
Surgery is rarely performed because of the risk of serious complications.
- recurrence of pain;
- false alliance;
- Infect;
- Phlebitis of extremities;
- Violation of urination;
- Transplant-induced pain;
- Embedded fastener failure.
general advice
You cannot self-administer medications.